O09.01 | Sites, Symptoms, CT Scan Findings and Survival in Patients with Recurrence After Curative-Intent Surgical Resection for Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma
Authors: Hideki Ujiie, Daniel Buitrago, Kyuichi Kadota, James Huang, William D. Travis, Valerie W. Rusch, Prasad S. Adusumilli, Nabil P. Rizk
Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY/UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Background:
The purpose of this study is to examine the patterns of recurrence for stage I lung adenocarcinoma and to identify clinicopathologic factors associated with post-recurrence survival (PRS).
Methods:
We performed a retrospective review of 1027 patients with stage I lung adenocarcinoma who underwent a surgical resection between 1999 and 2009 (median follow-up 35 months). The manner of recurrence detection, either by scheduled CT scan, presentation with new symptoms, or by other means, was noted. Tumors were classified using the new IASLC/ATS/ERS nomenclature and grading as low (adenocarcinoma in situ, minimally invasive adenocarcinoma, or lepidic-predominant), intermediate (papillary-predominant or acinar-predominant), and high (micropapillary-predominant, solid-predominant, colloid-predominant, or invasive mucinous) grade. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to analyze recurrence-free survival (RFS). Log-rank tests and Cox proportional hazard models were used to analyze the association between predictive factors and PRS.
Results:
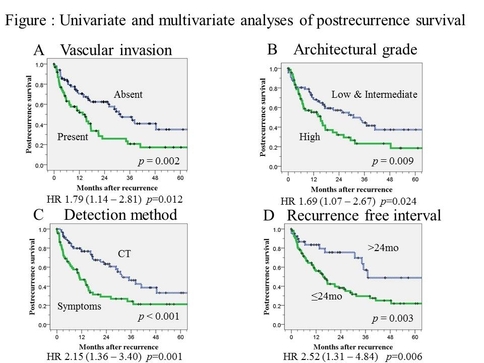
Of the 1027 patients with follow-up data available, 151(15%) had recurrent disease (table), five-year RFS was 80%. Of the 151 patients with recurrence, 80 (52%) were detected by a scheduled CT scan (51 locoregional and 29 distant). Symptomatic recurrences were seen in 70 (46%) patients (9 locoregional and 61 distant). Overall, 5-year PRS was 27.8%. On multivariate analysis, recurrences identified by new symptoms (HR, 2.15; 95% CI, 1.36- 3.40; p=0.001), a recurrence free interval ≤ 24 months (HR, 2.52; 95% CI, 1.31- 4.84; p=0.006), and tumors with high architectural grade (HR, 1.69; 95% CI, 1.07- 2.67; p=0.024) and vascular invasion (HR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.14- 2.81; p=0.012) were significantly associated with a worse PRS (Figure).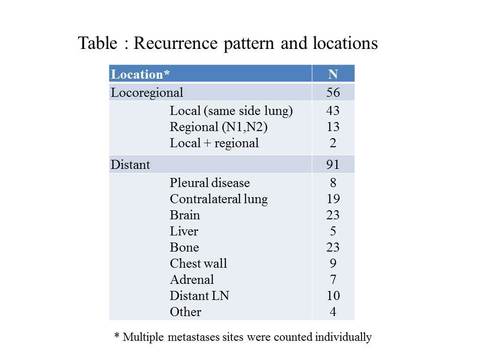
Conclusion: