12月12日,默沙东(MSD)宣布,抗PD-1疗法Keytruda单药一线治疗肿瘤表达PD-L1(肿瘤比例评分[TPS]≥1%)的转移性非鳞状非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)患者,表现出总生存期(OS)、无进展生存期(PFS)和客观缓解率(ORR)的改善,无论KRAS突变状态如何。这些结果是基于关键性3期KEYNOTE-042试验的探索性分析,今天在瑞士日内瓦2019年欧洲肿瘤内科学会(ESMO)免疫肿瘤学大会上发表了论文(摘要#LBA4)。
探索性分析的目的是评估KRAS突变的患病率及其与KEYNOTE-042试验中疗效的相关性。在入组KEYNOTE-042且肿瘤表达PD-L1(TPS≥1%)的1,274例未接受治疗的转移性非鳞状NSCLC患者中,301例患者具有KRAS可评价数据(n=232,无任何KRAS突变;n=69,有任何KRAS突变,包括n=29,KRAS G12C突变)。通过肿瘤组织和对应的正常DNA(血液)的全外显子组测序(WES)确定组织肿瘤突变负荷(tTMB)和KRAS突变状态。患者以1:1的比例随机接受Keytruda 200mg静脉注射,每三周一次(Q3W)(n=637)或研究者选择的化疗(培美曲塞或紫杉醇)(n=637)。治疗持续至疾病进展或出现不可接受的毒性。主要终点为OS,TPS≥50%、≥20%和≥1%,依次评估。次要终点为PFS和ORR。
这项探索性分析的结果显示,在转移性非鳞状NSCLC患者中,与化疗相比,Keytruda单药疗法可改善临床结局,无论KRAS突变状态如何。在这项分析中,与化疗相比,Keytruda使任何KRAS突变患者的死亡风险降低58%(HR=0.42[95%CI,0.22-0.81]),使KRAS G12C突变患者的死亡风险降低72%(HR=0.28[95%CI,0.09-0.86])。Keytruda的安全性与之前报告的转移性NSCLC患者研究中观察到的结果一致。
该探索性分析的其他疗效结果显示:
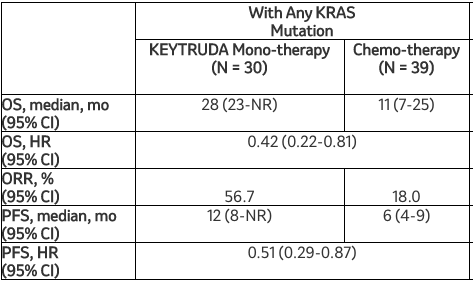
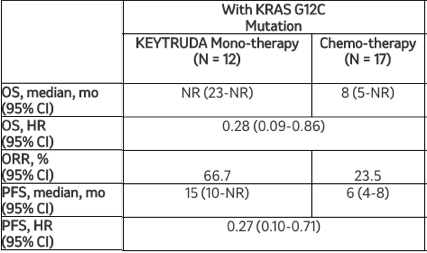
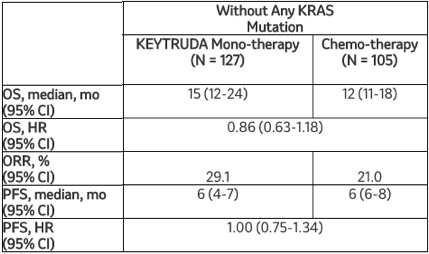
默沙东研究实验室肿瘤临床研究副总裁Jonathan Cheng博士说:“KRAS突变发生在大约20%的非小细胞肺癌患者中,之前的一些研究提示这些突变与较差的治疗反应相关。因此,在这项探索性分析中看到Keytruda单药治疗与某些转移性非鳞状非小细胞肺癌患者的生存获益相关是令人鼓舞的,无论KRAS突变状态如何。”
KEYNOTE-189(摘要#LBA5)的探索性分析数据,评价了KRAS突变及其与Keytruda联合培美曲塞和铂类药物化疗的疗效结局的相关性,今天在2019年ESMO免疫肿瘤学大会的一个小型口头报告会议上也展示了该数据。KEYNOTE-189是与培美曲塞(力比泰®)生产商礼来(Eli Lilly and Company)合作开展。



