
2019-04-12
作者:广东省肺癌研究所 杨学宁 & LAMP
非小细胞肺癌根治性化疗±放疗后局部复发的挽救性切除后的生存
313. Survival After Salvage Resection for Locally Recurrent Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Following Definitive Chemo and/or Radiotherapy (CRT): A Case-Matched Comparison
Matthew Curtis Woods, Trevor A. Davis, Aravind Krishnan, Ved Anand Tanavde, *Stephen Clyde Yang
The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD
Invited Discussant: *Young Tae Kim
Objective: Clinical data of patients who have undergone salvage lung cancer resection for locally recurrent NSCLC after definitive CRT is limited. The aim of this study is to assess morbidity and mortality of salvage lung resection, and to compare long-term survival to a matched trimodality cohort.
Methods: A single-institution retrospective review was performed on patients who underwent definitive CRT for NSCLC from 2001-2015, and then underwent salvage pulmonary resection for local recurrence. A salvage operation was defined as a resection greater than 56 days after definitive chemo and/or radiotherapy. Five-year survival, 30-and 90-day mortality were calculated. A case-matched cohort consisting of patients who had undergone resection and underwent adjuvant therapy was developed by closely matching age, tumor stage and histology.
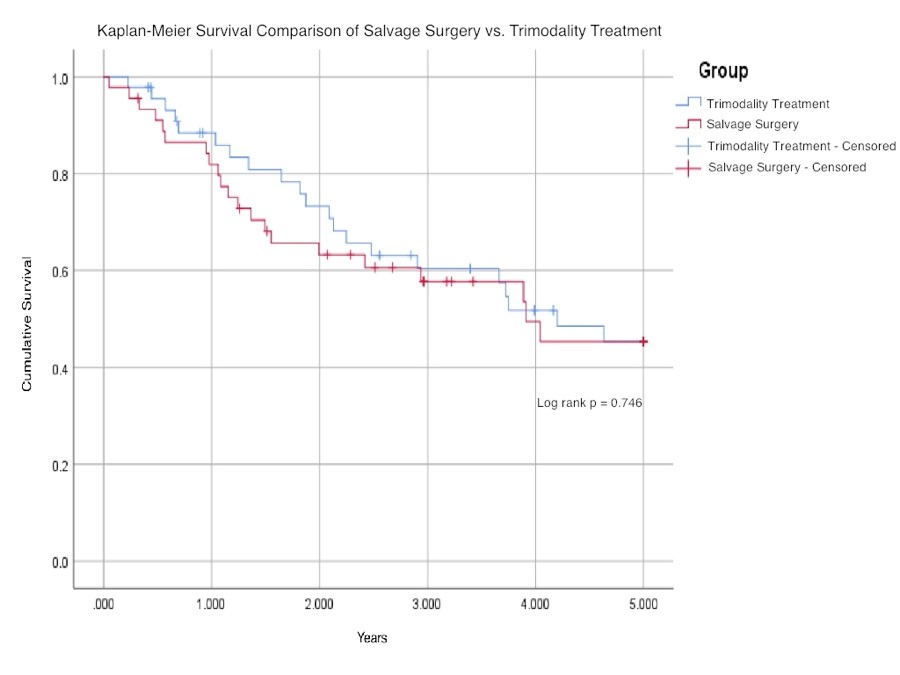
Results: Among the 45 patients undergoing salvage lung resection, average age was 62 years, with 23 (51%) females. Prior to resection, three received radiation alone, 16 chemotherapy alone, and 26 combination therapy. Resections included six pneumonectomies, 34 lobectomies, and five sublobar resections. Ninety-day mortality was 2% (1). In the case-matched cohort (n=45) average age was 62 years, with 22 (49%) females; adjuvant therapy included 2 radiation alone, 37 chemotherapy alone, and 6 combination chemoradiotherapy. The five-year Kaplan-Meier survival curves are shown (Figure 1). Median survival of the salvage and trimodality groups were 3.9 and 4.2 years, respectively (P=.44). The Kaplan-Meier survival of the two groups at 5 years was the same. Among the 45 patients undergoing salvage lung resection, average age was 62 years, with 23 (51%) females. Prior to resection, three received radiation alone, 16 chemotherapy alone, and 26 combination therapy. Resections included six pneumonectomies, 34 lobectomies, and five sublobar resections. Ninety-day mortality was 2% (1). In the case-matched cohort (n=45) average age was 62 years, with 22 (49%) females; adjuvant therapy included 2 radiation alone, 37 chemotherapy alone, and 6 combination chemoradiotherapy. The five-year Kaplan-Meier survival curves are shown (Figure 1). Median survival of the salvage and trimodality groups were 3.9 and 4.2 years, respectively (P=.44). The Kaplan-Meier survival of the two groups at 5 years was the same.
Conclusions: Salvage lung resection offers comparable median and five-year survival to conventional trimodality therapy. In the properly selected patient, this may represent a potential option for lung cancer patients who fail definitive chemo- and/or radiation.
Table 1 - Demographics and Median Survival | |||
Group | Median Age | Sex | Median Survival |
Trimodality Treatment | 62.3 | 22 females, 23 males | 4.2 |
Salvage Lung Resection | 61.6 | 23 females, 22 males | 3.9 |
目的
对根治性CRT后局部复发的NSCLC患者进行挽救性切除的临床研究鲜有报道。本研究的目的是评估挽救性肺切除术的发病率和死亡率,并将长期生存率与匹配传统的三联治疗(化疗、放疗、手术治疗)进行比较。
方法
针对2001~2015年经根治性CRT后局部复发并接受挽救性肺切除术的NSCLC患者进行了一项单机构回顾性研究。将根治性CRT后超过56 d进行的手术定义为挽救性手术。统计30 d和90 d的死亡率并建立了一组病例匹配队列,对接受挽救性手术以及辅助治疗的患者进行年龄、肿瘤分期和组织学的匹配。
结果
45例患者接受了挽救性肺切除术,平均年龄为62岁,其中23例(51%)为女性。在手术之前,3例接受了单纯放疗、16例接受了单纯化疗、26例接受了联合放化疗。手术包括了6例全肺切除术、34例肺叶切除术和5例亚肺叶切除术。90 d死亡率是2%。病例匹配队列(n=45)平均年龄为62岁,22例(49%)女性;辅助治疗包括2例单纯放疗、37例单纯化疗和6例联合放化疗。5年Kaplan-Meier 生存曲线见表1。挽救性手术组和传统三联治疗组的中位生存期分别为3.9和4.2年(P=0.44)。两组患者的5年Kaplan-Meier 生存率相同。
表1. 病例资料和中位生存
结论
挽救性手术与传统三联治疗的中位和五年生存率相当。在适当选择的患者中,挽救性手术可能是根治性CRT失败患者的一个潜在选择。
推荐阅读
文章评论
注册或登后即可发表评论
登录/注册
全部评论(0)